S M Kamrul Hasan
|
 |
S M Kamrul Hasan
|
 |
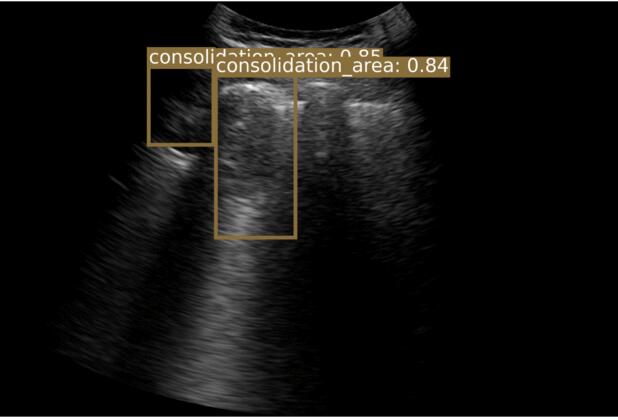
I’m a Senior AI Scientist at Johnson & Johnson. I have 8+ years of experience designing and deploying scalable, high-impact AI solutions in computer vision, multi-modal learning, and foundation models. I specialize in self-supervised learning, model compression, and multi-modal AI, driving state-of-the-art advancements in medical imaging and AI-powered drug discovery. I finished my PhD from Chester F. Carlson Center for Imaging Science at Rochester Institute of Technology (RIT), Rochester, NY under the direction of my advisor, Dr. Cristian Linte, funded by NSF and NIH grants. My PhD thesis focused on deep learning architectures for segmentation in medical imaging. I worked at Philips Research designing an optimized object detection framework for COVID-19 lung ultrasound, and at IBM Research on deep neural network pruning/optimization for explainable AI.
From fully-supervised single-task learning to semi-supervised multi-task deep learning for robust clinical segmentation.
End-to-end systems: data → model → evaluation → deployment, with an emphasis on reliability and measurable impact.
Filter by year • Expand for more

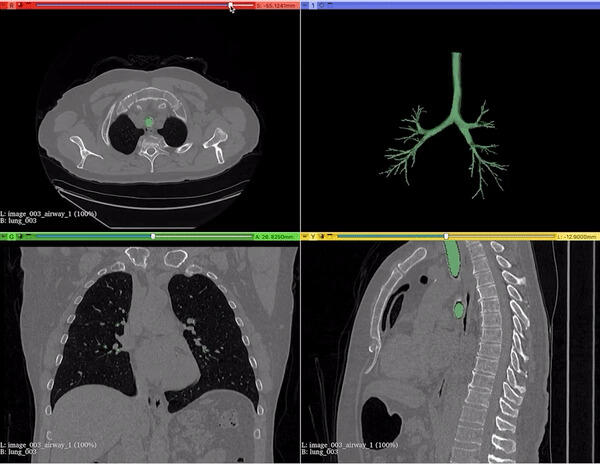





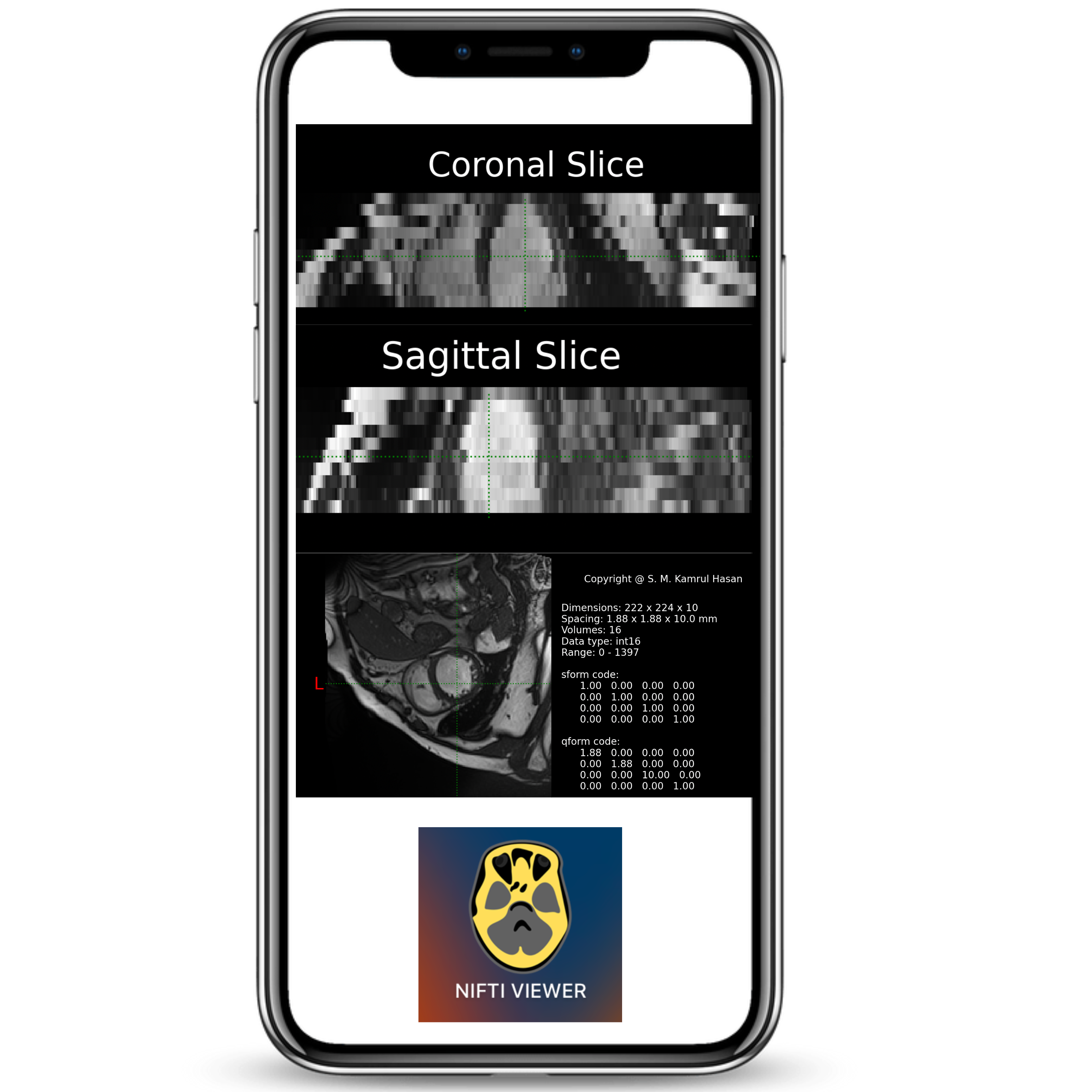
Designed and built a native macOS application to visualize NiFTI neuroimaging files, enabling intuitive exploration of volumetric medical data across coronal, sagittal, and axial planes.
Focused on performance, usability, and clean rendering for research workflows in medical imaging.
Download Software →
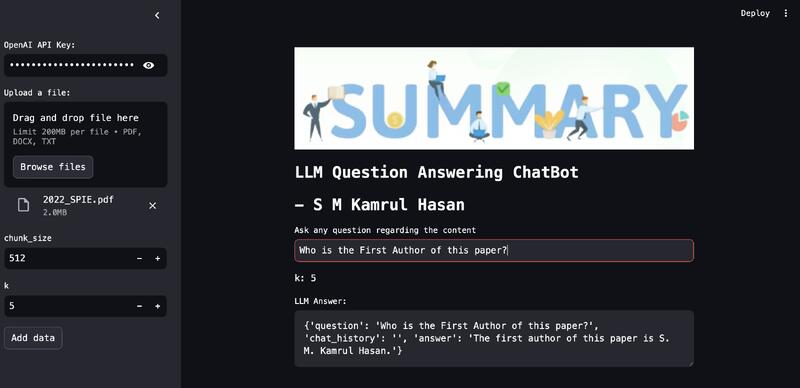
Built a GenAI-powered summarization chatbot capable of extracting concise, high-quality summaries from PDFs, DOCX, TXT files, and Wikipedia articles.
Uses embedding-based retrieval and context-aware prompting to provide accurate, source-grounded responses.
Download Software →
|
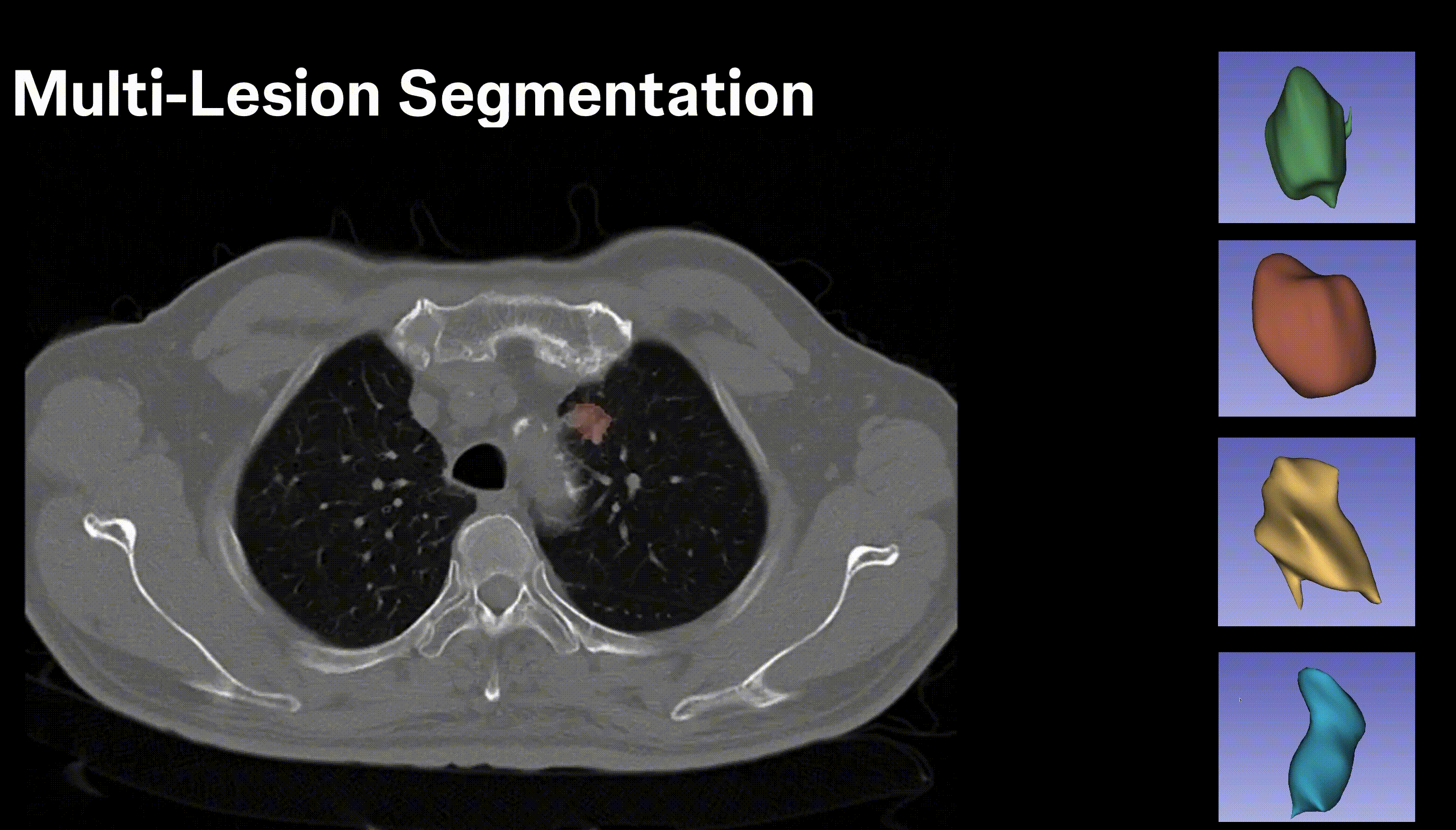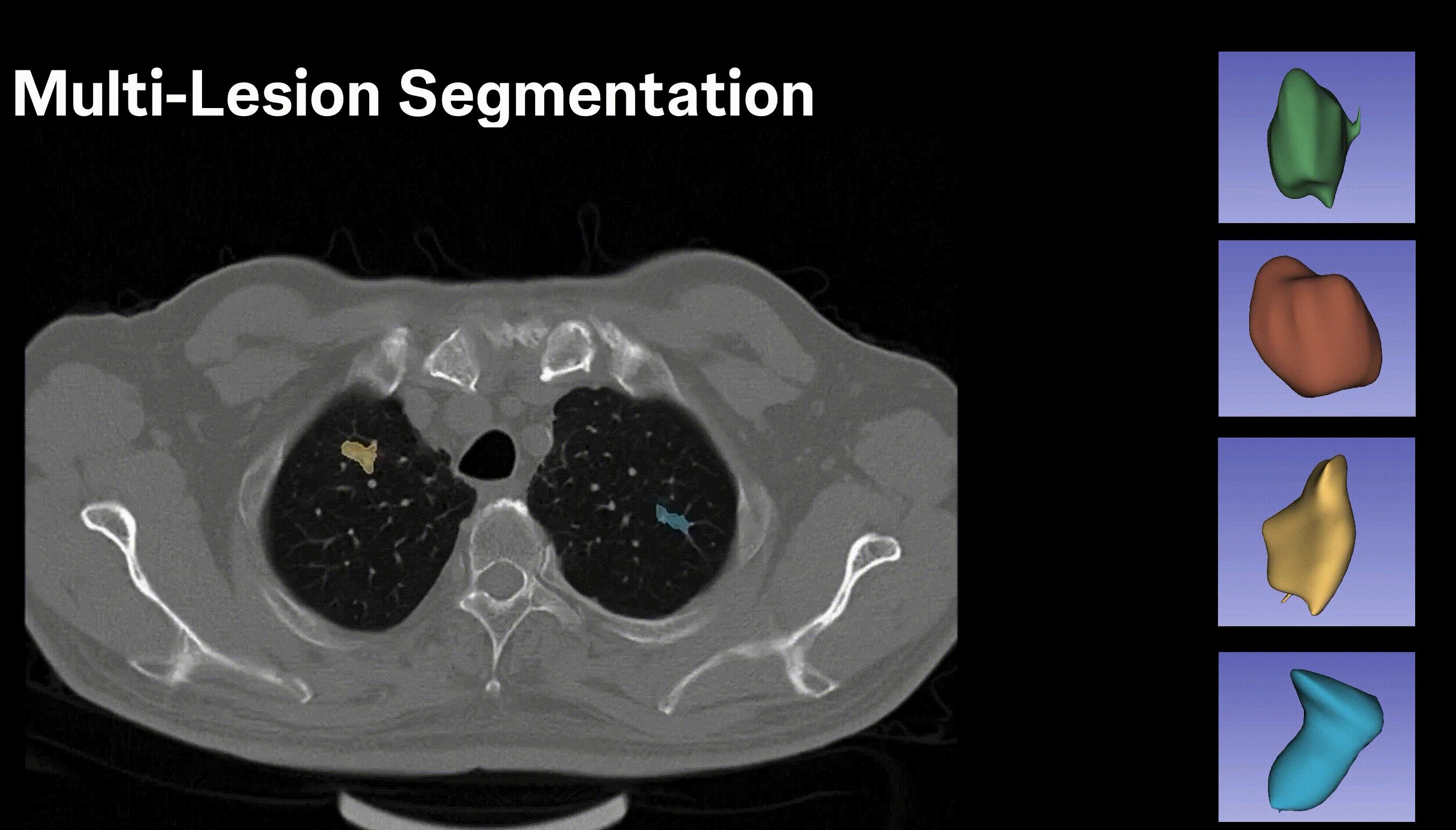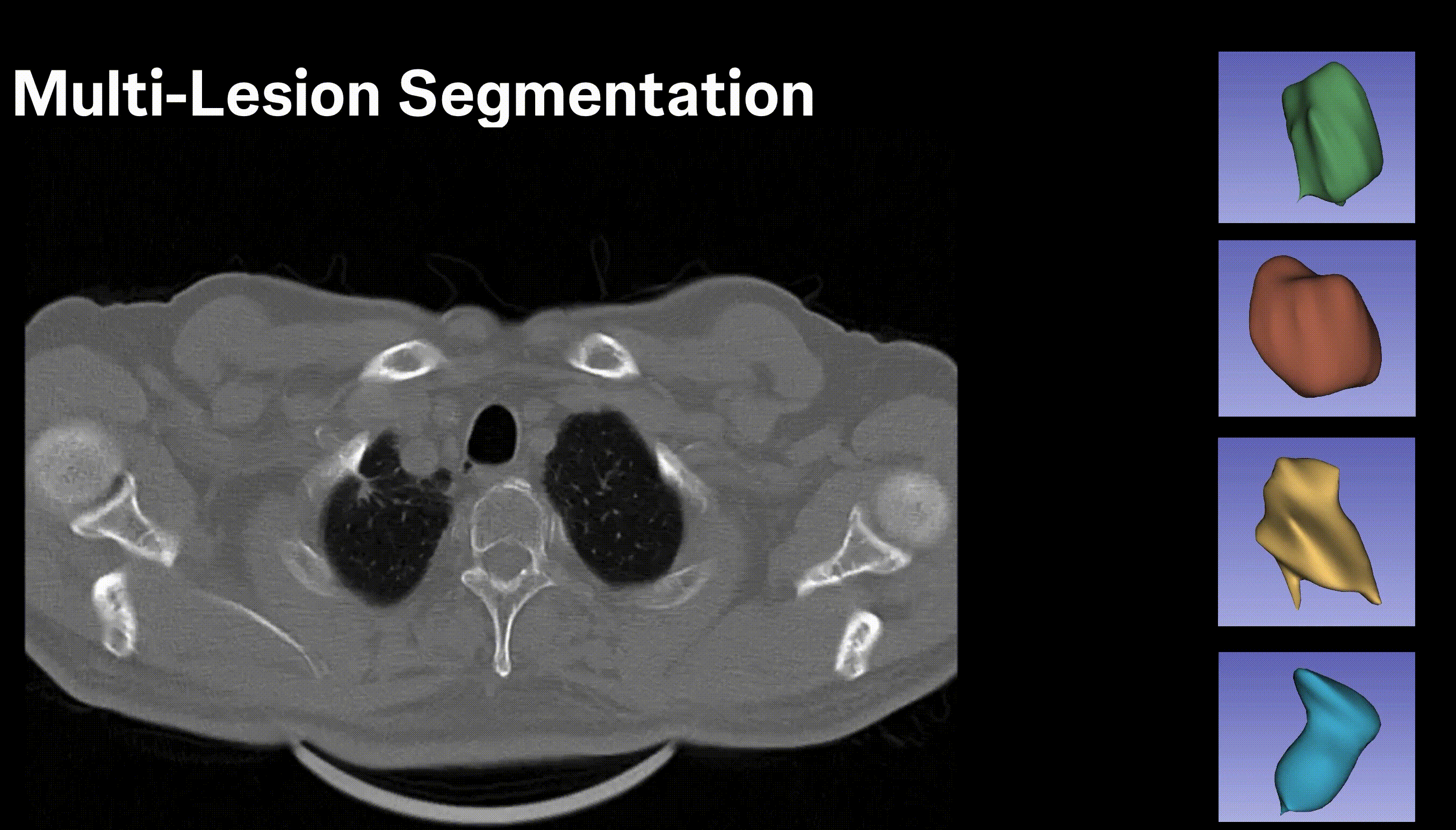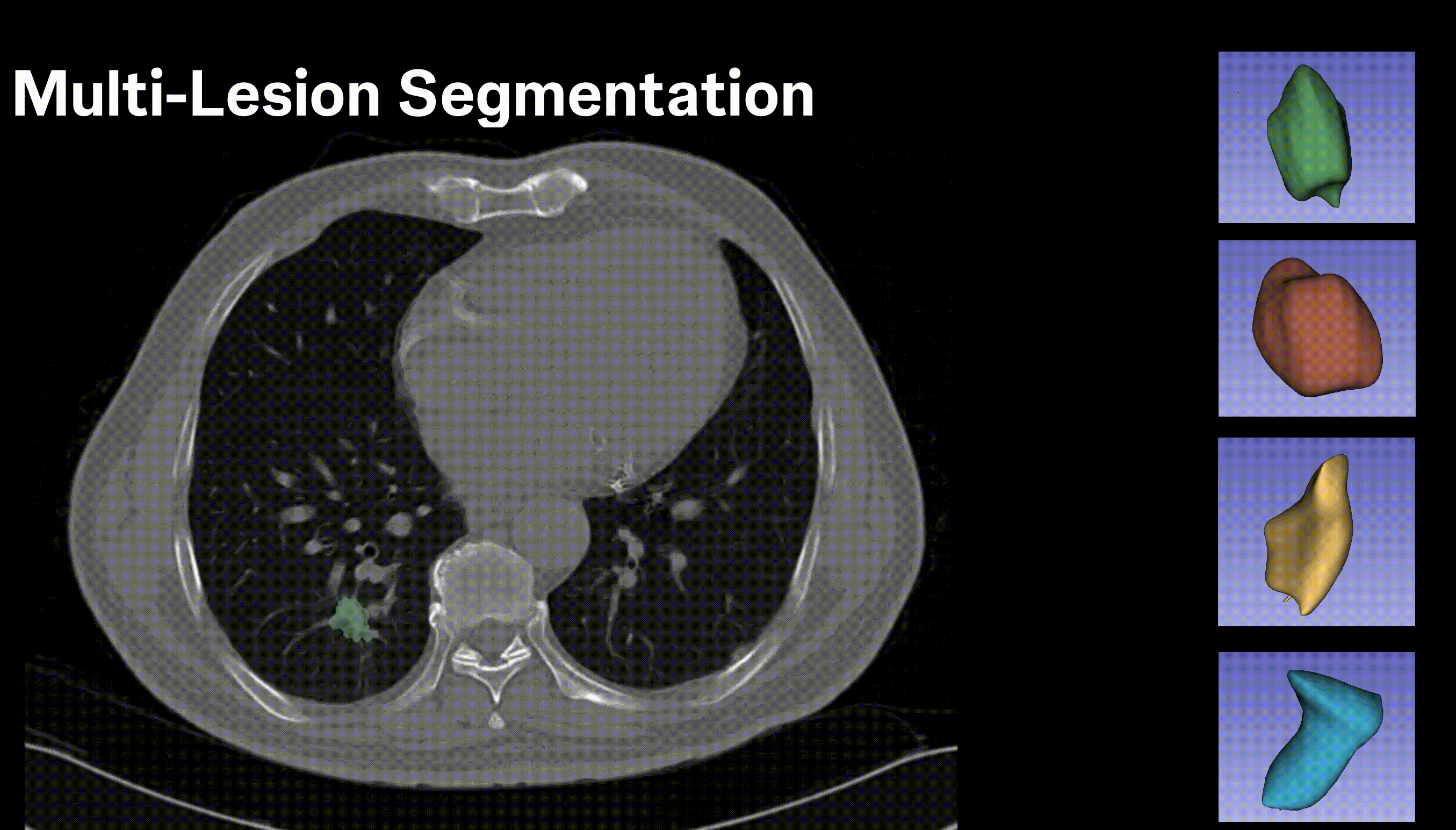
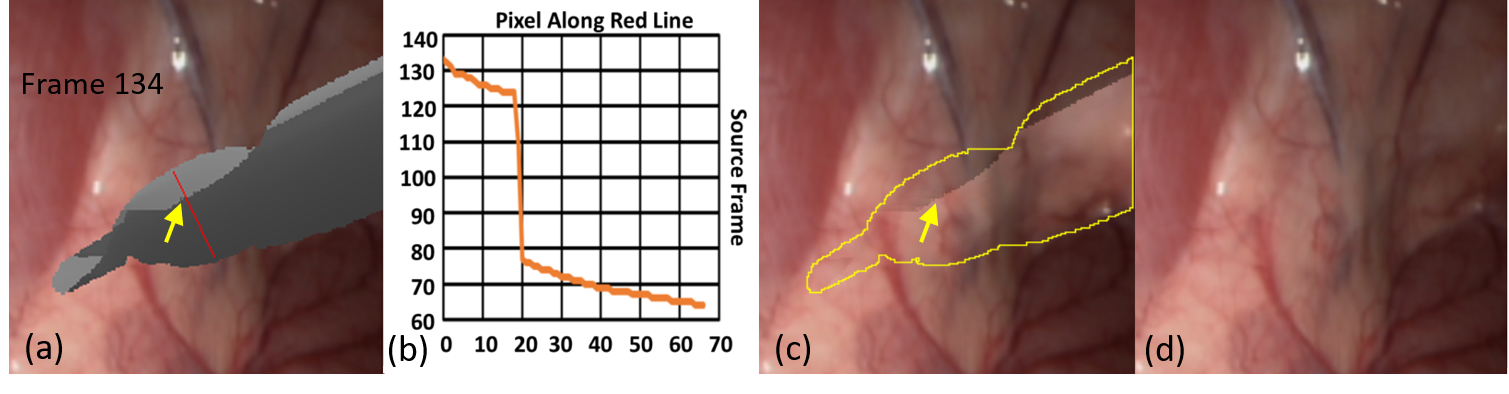
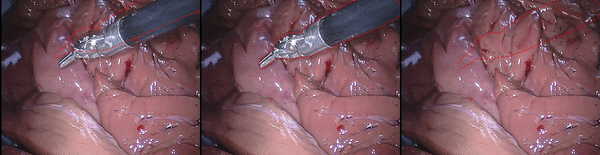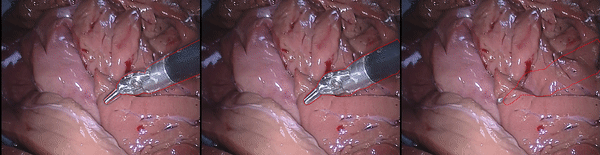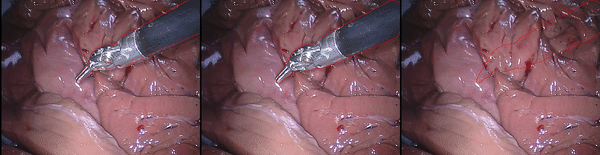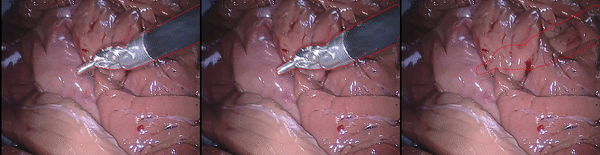
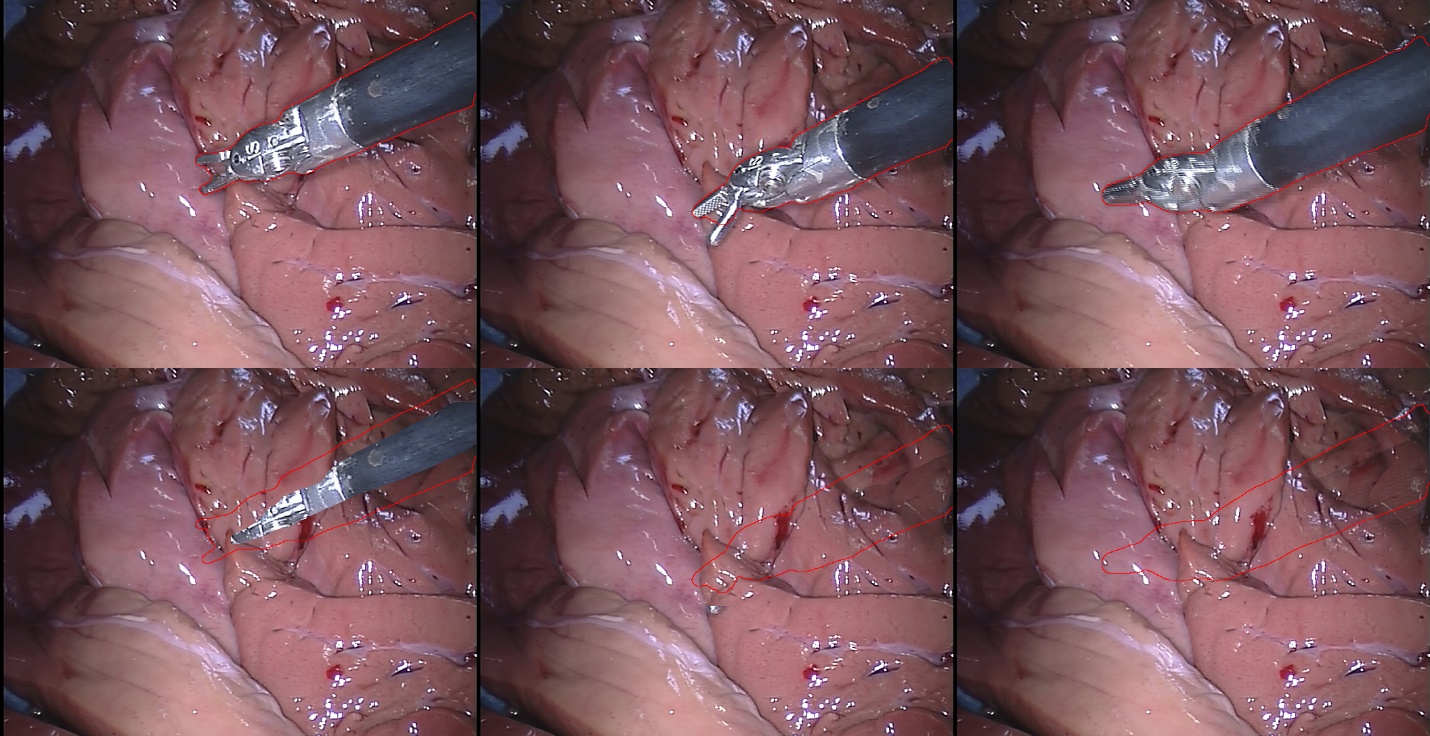
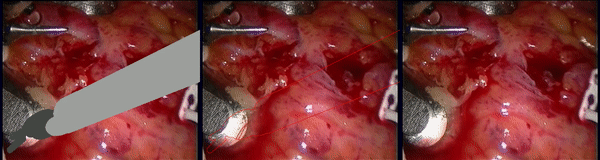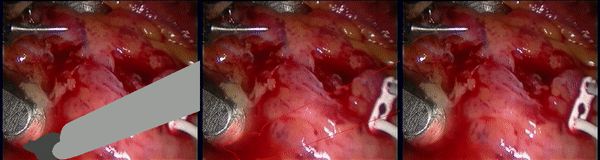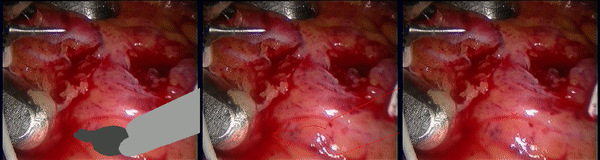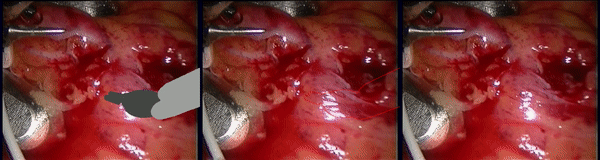
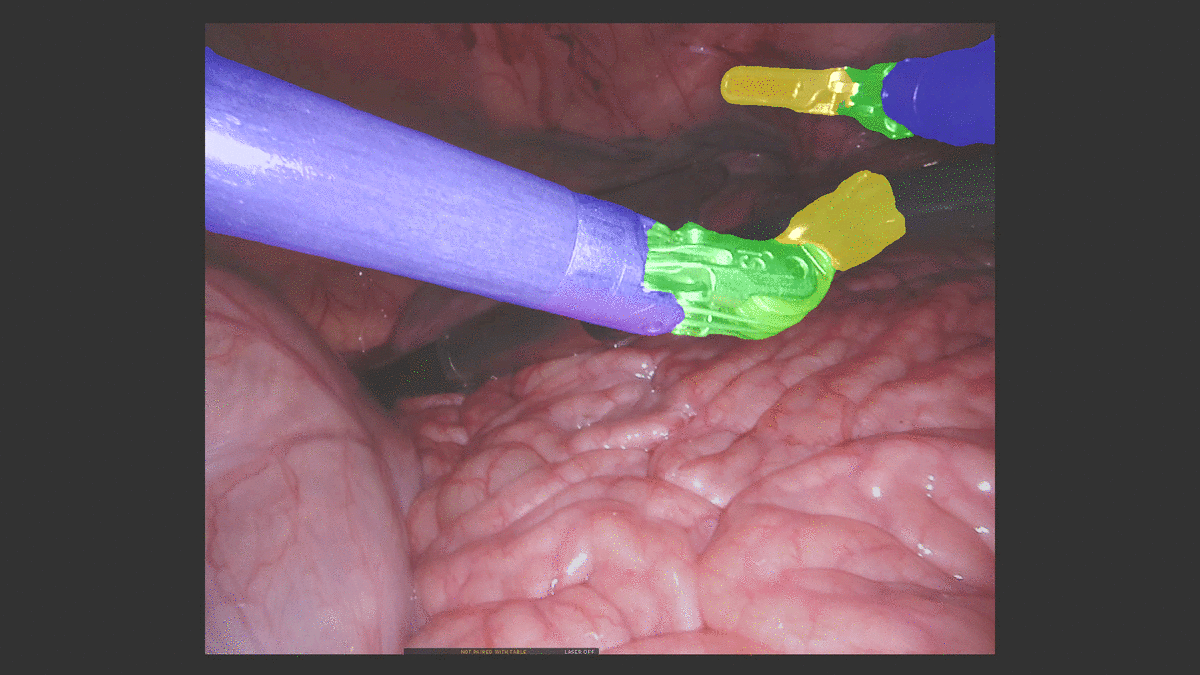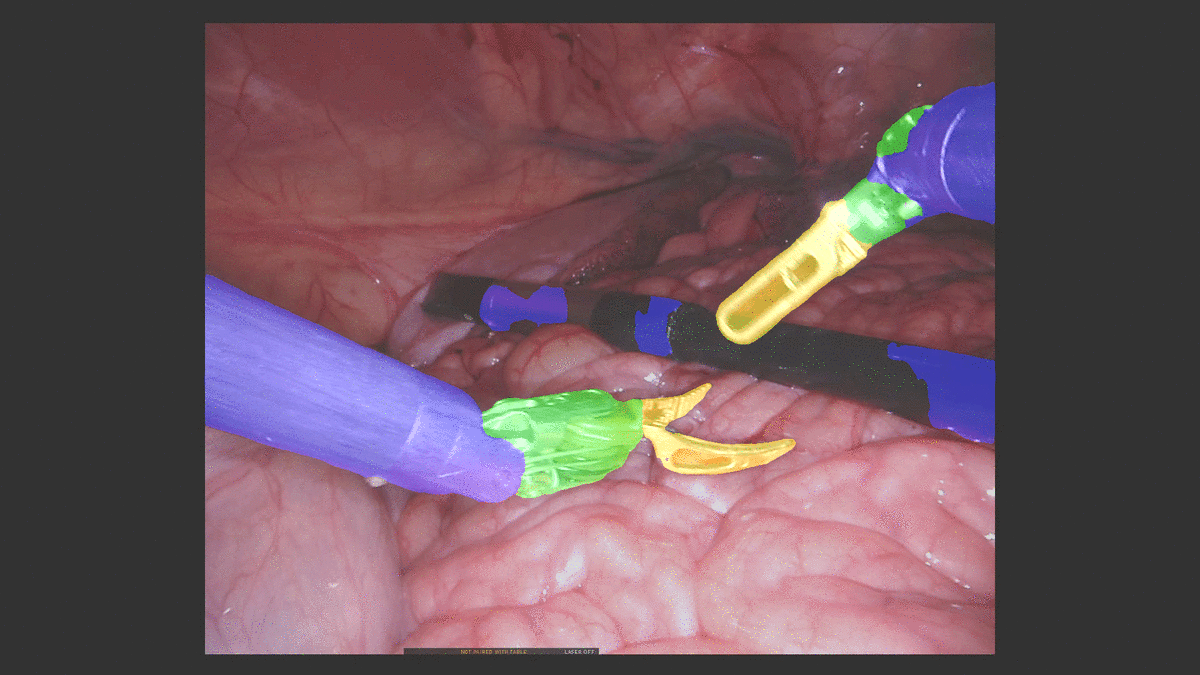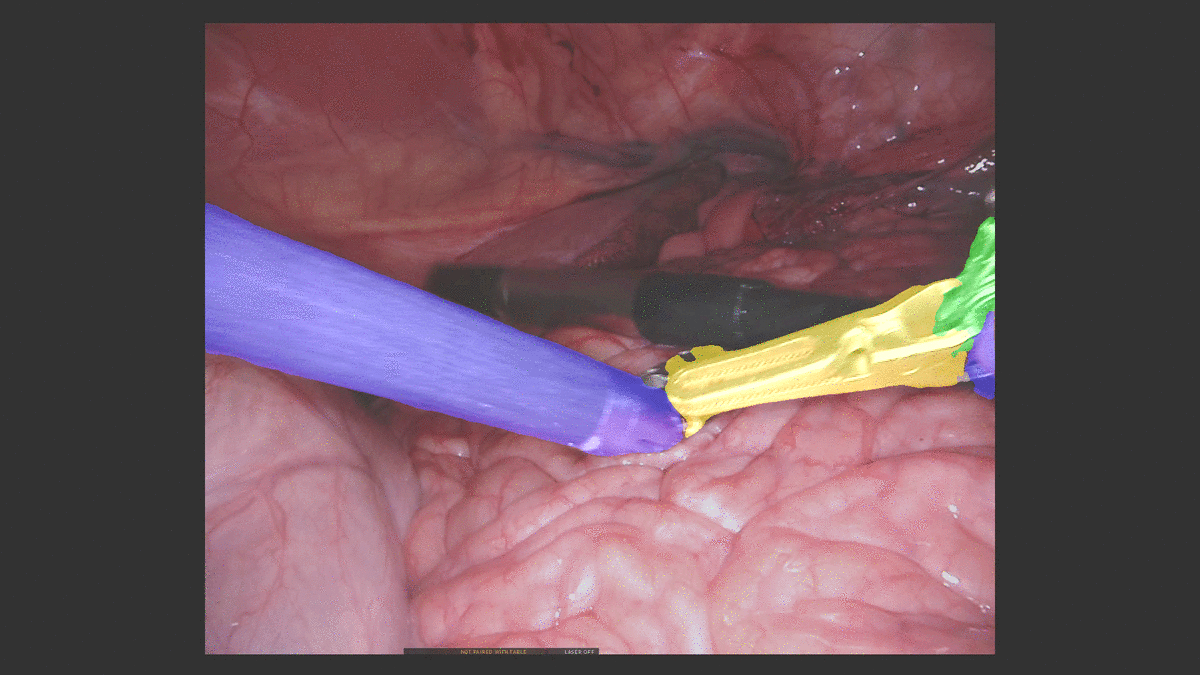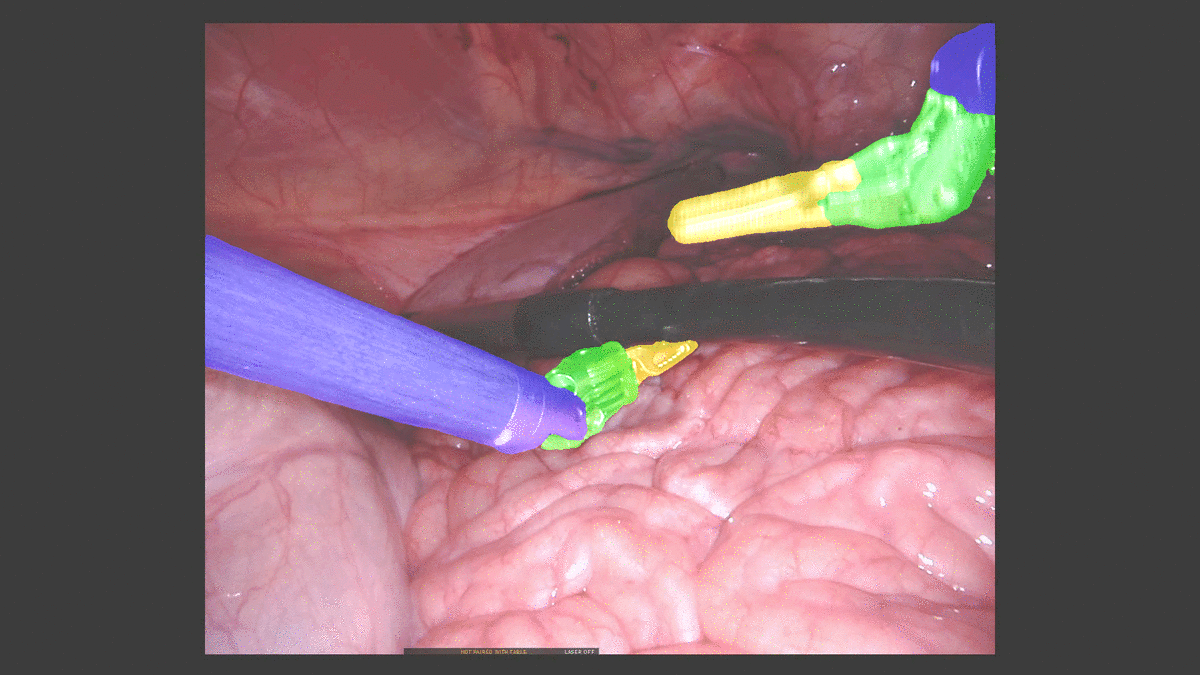
Inpainting Surgical Occlusion from Laparoscopic Video Sequences for Robot-assisted Interventions Journal of Medical Imaging , 2023 [paper][code][dataset][bibtex][Video 1] With the aid of digital inpainting algorithms, this paper presents a novel application that uses image segmentation to remove surgical instruments from laparoscopic/endoscopic video. |

|
Learning Deep Representations of Cardiac Structures for 4D Cine MRI Image Segmentation through Semi-supervised Learning Applied Science , 2022 [paper][code][dataset][bibtex][Video 1] In this paper, we propose a semi-supervised model --- namely, Combine-all in Semi-Supervised Learning (CqSL) --- to demonstrate the power of a simple combination of a disentanglement block, variational autoencoder (VAE), generative adversarial network (GAN), and a conditioning layer-based reconstructor for performing two important tasks in medical imaging: segmentation and reconstruction. Our work is motivated by the recent progress in image segmentation using semi-supervised learning (SSL), which has shown good results with limited labeled data and large amounts of unlabeled data. |

|
The impact of class-dependent label noise in medical image (MedMNIST dataset) classification SPIE Medical Imaging -- Image Processing , 2023 [paper][code][dataset][bibtex][Video 1] In this paper, we study this hypothesis using two publicly available datasets: a 2D organ classification dataset with target organ classes being visually distinct, and a histopathology image classification dataset where the target classes look very similar visually. Our results show that the label noise in one class has much higher impact on the model's performance on other classes for histopathology dataset compared to the organ dataset. |
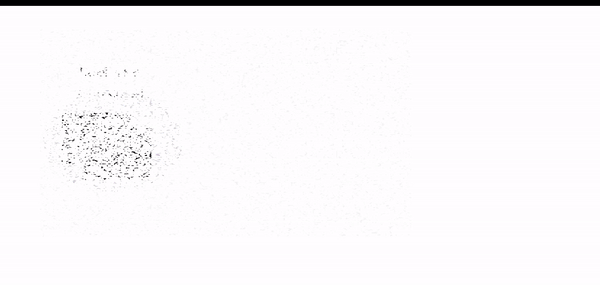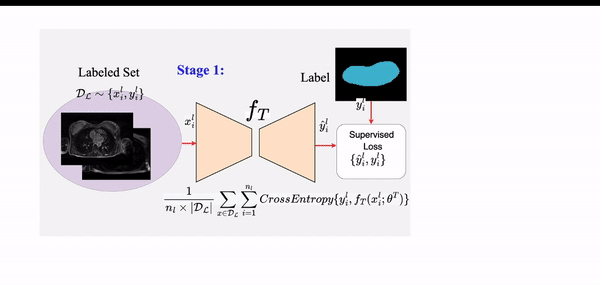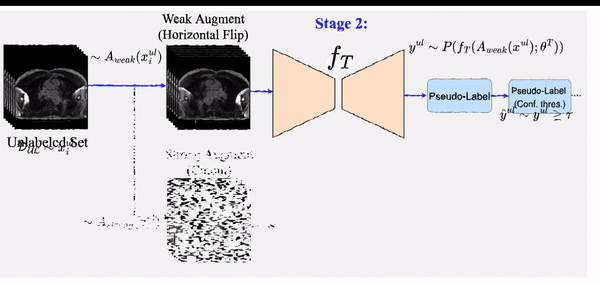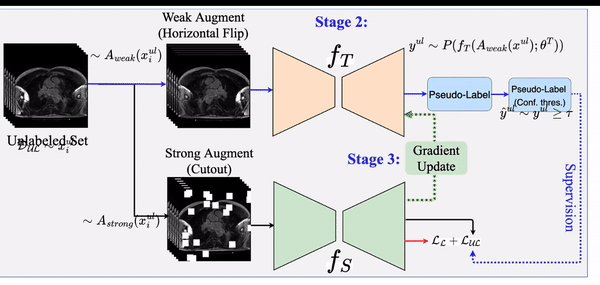
|
STAMP: A Self-training Student-Teacher Augmentation-driven Meta Pseudo-labeling Framework for 3D Cardiac MRI Image Segmentation S. M. Kamrul Hasan and Cristian A. Linte. Medical Image Understanding and Analysis (MIUA) , 2022 oral [paper][code][dataset][bibtex][Video 1] The proposed method uses self-training (through meta pseudo-labeling) in concert with a Teacher network that instructs the Student network by generating pseudo-labels given unlabeled input data. Meta pseudo-labeling methods allow the Teacher network to constantly adapt in response to the performance of the Student network on the labeled dataset, hence enabling the Teacher to identify more effective pseudo-labels to instruct the Student. Moreover, to improve generalization and reduce error rate, we apply both strong and weak data augmentation policies, to ensure the segmentor outputs a consistent probability distribution regardless of the augmentation level. |

|
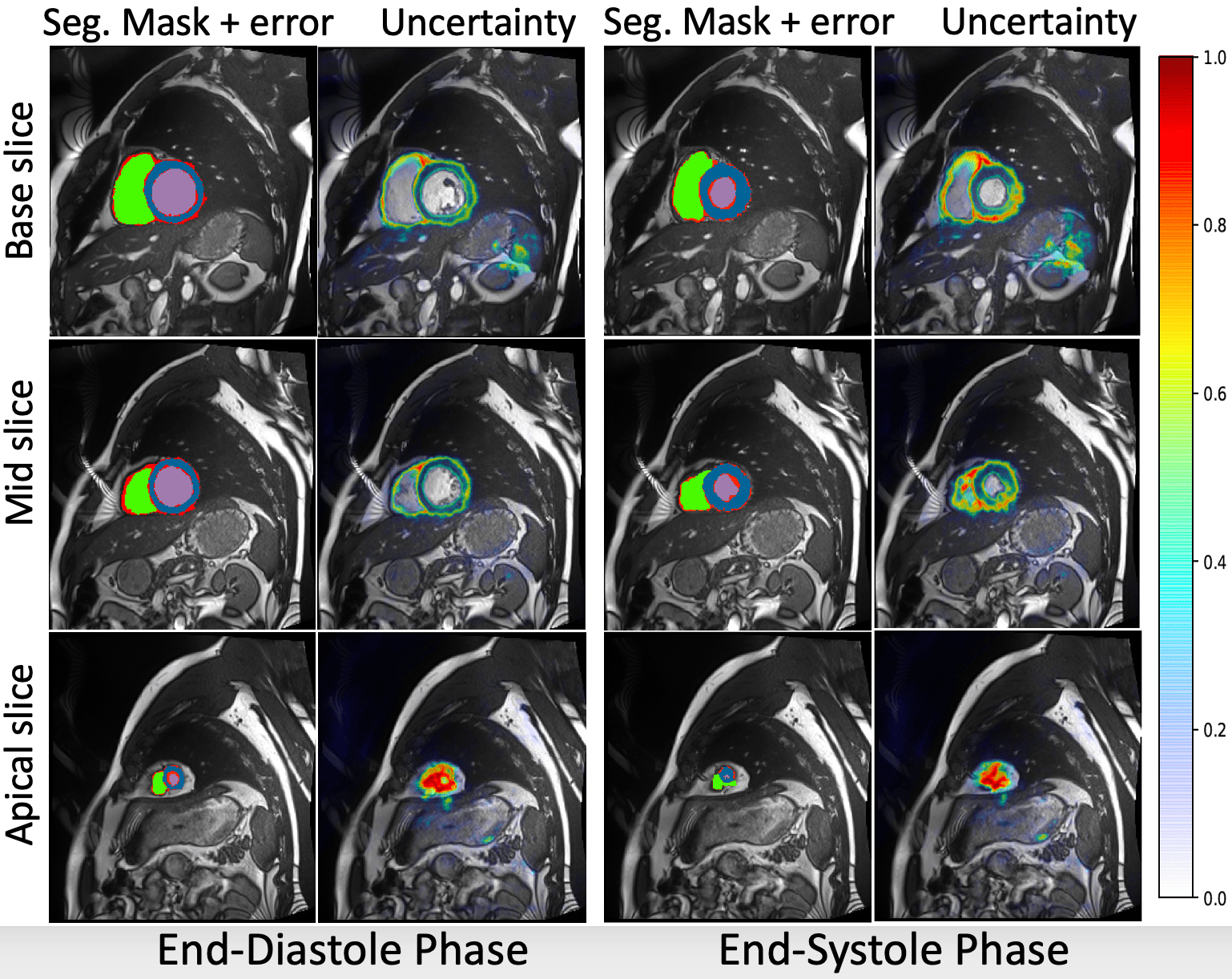
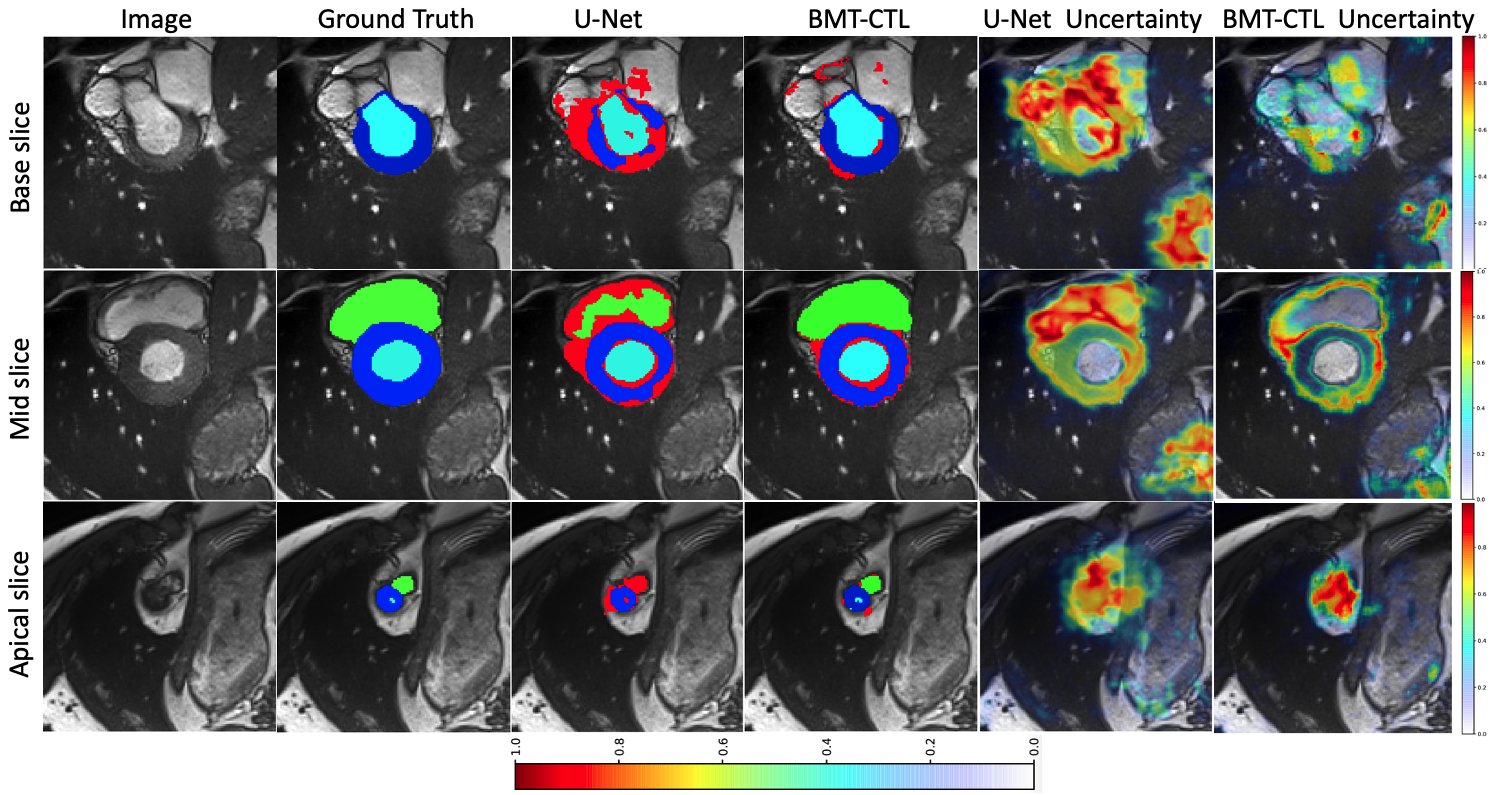
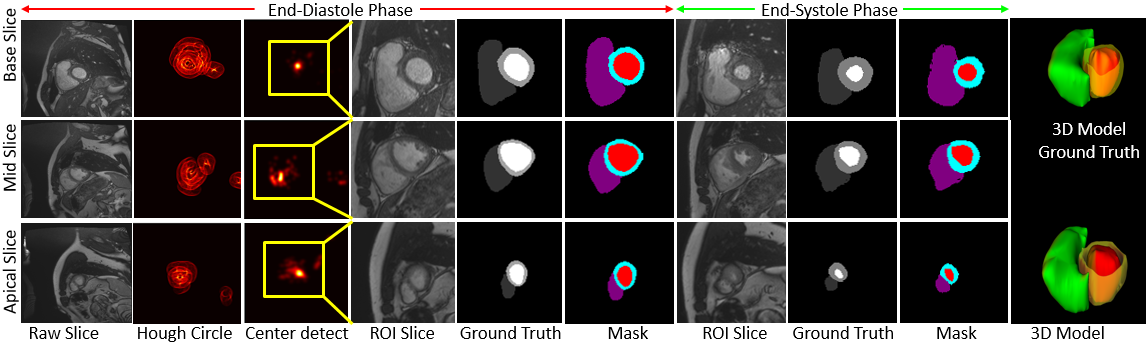
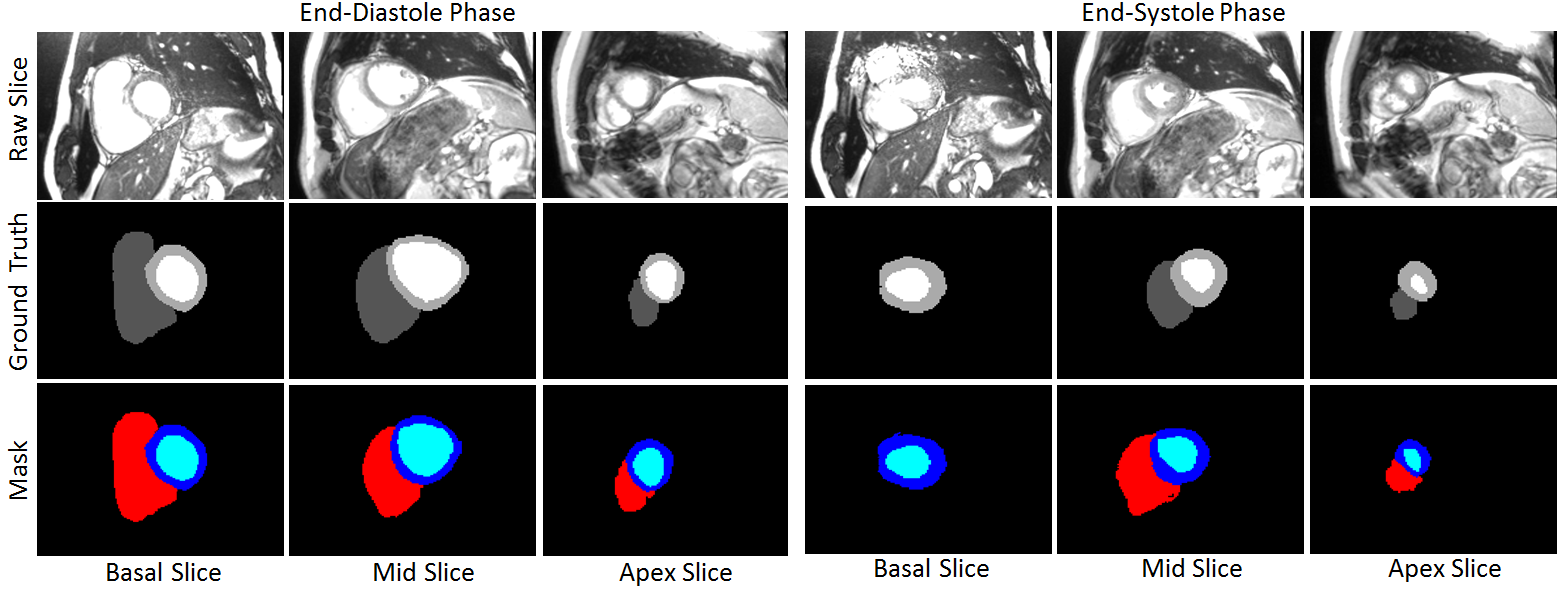
Joint Segmentation and Uncertainty Estimation of Ventricular Structures from Cardiac MRI using Probability Calibration S. M. Kamrul Hasan and Cristian A. Linte. International Conference of the Eng. in Med. & Bio (EMBC), 2022 oral [paper][code][dataset][bibtex][Video 1] In this work, we used a Bayesian version of our previously proposed CondenseUNet framework featuring both a learned group structure and a regularized weight-pruner to reduce the computational cost in volumetric image segmentation and help quantify predictive uncertainty. Our study further showcases the potential of our deep-learning framework to evaluate the correlation between the uncertainty and the segmentation errors for a given model. The proposed model was trained and tested on the Automated Cardiac Diagnosis Challenge (ACDC) dataset featuring 150 cine cardiac MRI patient dataset for the segmentation and uncertainty estimation of the left ventricle (LV), right ventricle (RV), and myocardium (Myo) at end-diastole (ED) and end-systole (ES) phases. |
|
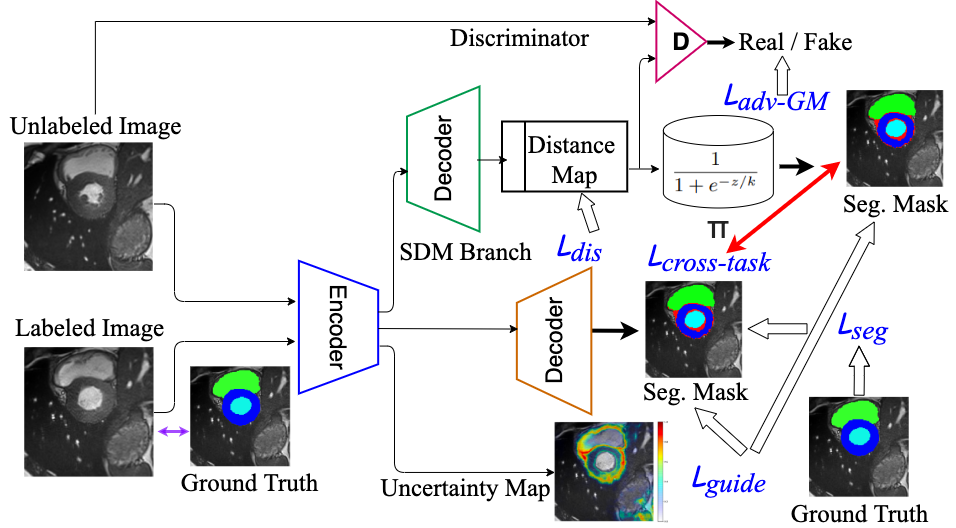
Calibration of cine MRI segmentation probability for uncertainty estimation using a Multi-Task Cross-Task Learning architecture. S. M. Kamrul Hasan and Cristian A. Linte. SPIE Medical Imaging, 2022 oral [paper][code][dataset][bibtex][Video 1] In this work we propose a novel method that incorporates uncertainty estimation to detect failures in the segmentation masks generated by CNNs, our study further showcases the potential of our model to evaluate the correlation between the uncertainty and the segmentation errors for a given model. Furthermore, we introduce a multi-task Cross-task learning consistency approach to enforce the correlation between the pixel-level (segmentation) and the geometric-level (distance map) tasks. Our study serves as a proof-of-concept of how uncertainty measure correlates with the erroneous segmentation generated by different deep learning models, further showcasing the potential of our model to flag low-quality segmentation from a given model in our future study. |

|
Motion Extraction of the Right Ventricle from 4D Cardiac Cine MRI Using A Deep Learning-Based Deformable Registration Framework. Roshan Reddy Upendra*, S. M. Kamrul Hasan*, Richard Simon, Brian Jamison Wentz, Suzanne M. Shontz, Michael S. Sacks, and Cristian A. Linte. "The first two authors share equal joint first authorship" International Conference of the Engineering in Medicine & Biology Society (EMBC), 2021, oral [paper][code][dataset][bibtex][Video 1] In this work, we describe the development of dynamic patient-specific right ventricle (RV) models associated with normal subjects and abnormal RV patients to be subsequently used to assess RV function based on motion and kinematic analysis. In our study, we use a deep learning-based deformable network that takes 3D input volumes and outputs a motion field which is then used to generate isosurface meshes of the cardiac geometry at all cardiac frames by propagating the end-diastole (ED) isosurface mesh using the reconstructed motion field. |

|
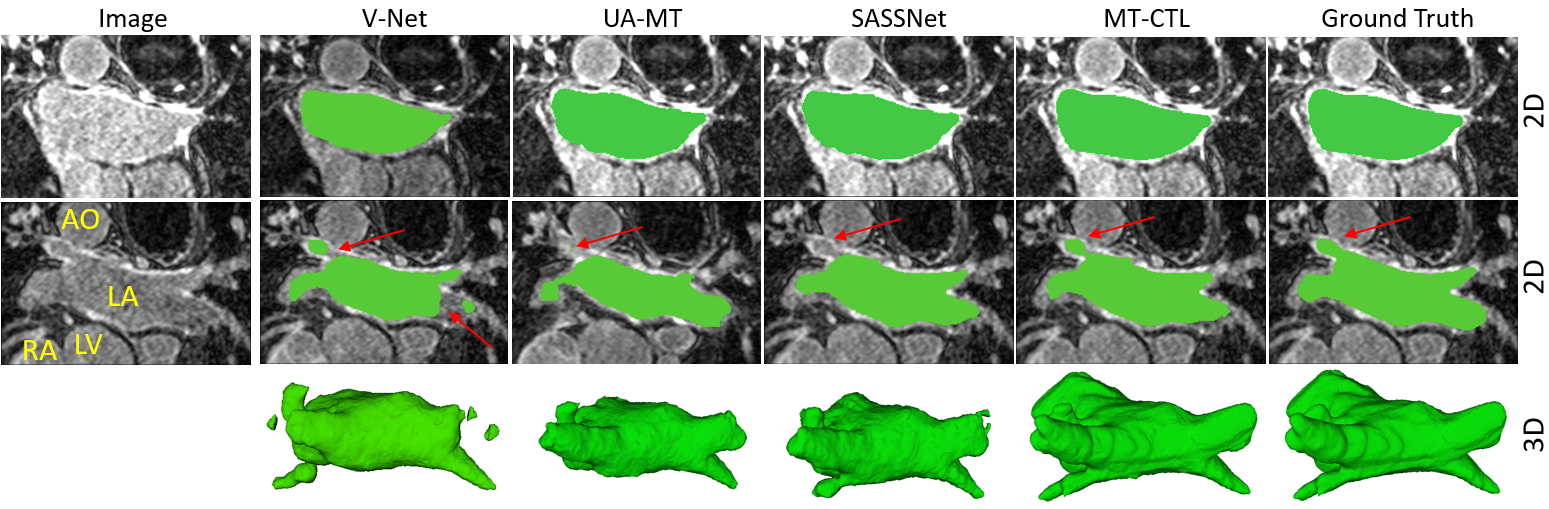
A Multi-Task Cross-Task Learning Architecture for Ad-hoc Uncertainty Estimation in 3D Cardiac MRI Image Segmentation. S. M. Kamrul Hasan and Cristian A. Linte. Computing in Cardiology , 2021, oral [paper][code][dataset][bibtex][Video 1] To generate smoother and accurate segmentation masks from 3D cardiac MR images, we present a Multi-task Cross-task learning consistency approach to enforce the correlation between the pixel-level (segmentation) and the geometric-level (distance map) tasks. Our extensive experimentation with varied quantities of labeled data in the training sets justify the effectiveness of our model for the segmentation of left atrial cavity from Gadolinium-enhanced magnetic resonance (GE-MR) images. With the incorporation of uncertainty estimates to detect failures in the segmentation masks generated by CNNs, our study further showcases the potential of our model to flag low quality segmentation from a given model. |
|
Segmentation and removal of surgical instruments for background scene visualization from Endoscopic / Laparoscopic video. S. M. Kamrul Hasan, Richard A. Simon, and Cristian A. Linte. SPIE Medical Imaging, 2021, oral [paper][code][dataset][bibtex][Video 1] [Video 2 ][Video 3] [Video 4] In this work, we implement a fully convolutional segmenter featuring both a learned group structure and a regularized weight-pruner to reduce the high computational cost in volumetric image segmentation. We validated our framework on the ACDC dataset featuring one healthy and four pathology groups imaged throughout the cardiac cycle. Based on these results, this technique has the potential to become an efficient and competitive cardiac image segmentation tool that may be used for cardiac computer-aided diagnosis, planning and guidance applications. |
|
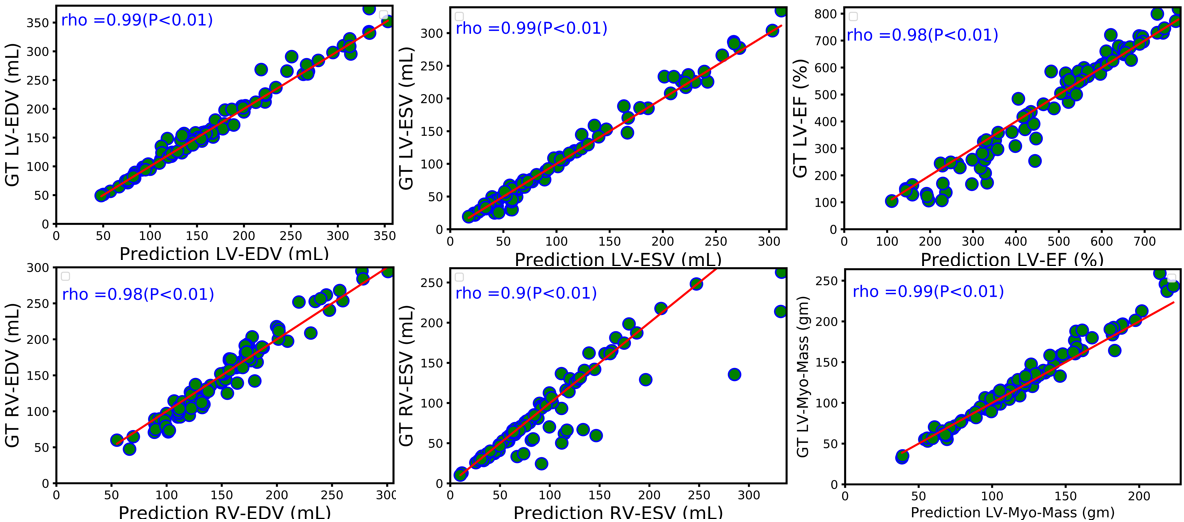
L-CO-Net: Learned Condensation-Optimization Network for Clinical Parameter Estimation from Cardiac Cine MRI. S. M. Kamrul Hasan, and Cristian A. Linte. International Conference of the Engineering in Medicine & Biology Society (EMBC), 2020, oral [paper][code][dataset][bibtex] In this work, we implement a fully convolutional segmenter featuring both a learned group structure and a regularized weight-pruner to reduce the high computational cost in volumetric image segmentation. We validated our framework on the ACDC dataset featuring one healthy and four pathology groups imaged throughout the cardiac cycle. Our technique achieved Dice scores of 96.8% (LV blood-pool), 93.3% (RV blood-pool) and 90.0% (LV Myocardium) with five-fold cross-validation and yielded similar clinical parameters as those estimated from the ground truth segmentation data. Based on these results, this technique has the potential to become an efficient and competitive cardiac image segmentation tool that may be used for cardiac computer-aided diagnosis, planning, and guidance applications. |


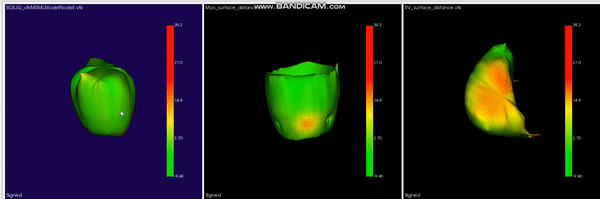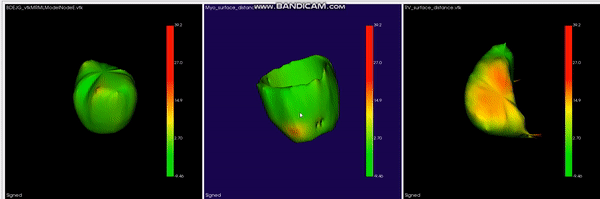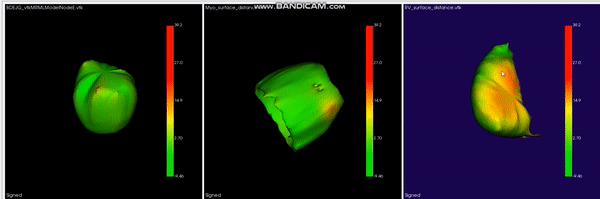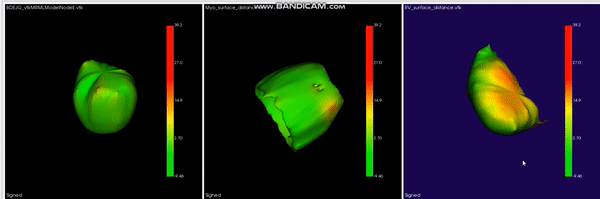
|
Learned Condensation-Optimization Network: A regularized Network for improved Cardiac Ventricles Segmentation on Breath-Hold Cine MRI. S. M. Kamrul Hasan, and Cristian A. Linte. International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (ISBI), 2020, oral [paper][code][dataset][bibtex] In this work, we implement a fully convolutional segmenter featuring both a learned group structure and a regularized weight-pruner to reduce the high computational cost in volumetric image segmentation. We validated the framework on the ACDC dataset and achieved accurate segmentation, leading to mean Dice scores of 96.80% (LV blood-pool), 93.33% (RV blood-pool), 90.0% (LV Myocardium) and yielded similar clinical parameters as those estimated from the ground-truth segmentation data. |

|
CondenseUNet: a memory-efficient condensely-connected architecture for bi-ventricular blood pool and myocardium segmentation. S. M. Kamrul Hasan, and Cristian A. Linte. SPIE Medical Imaging, 2020, oral [paper][code][dataset][bibtex] In this work, we propose a novel memory-efficient Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) architecture as a modification of both CondenseNet, as well as DenseNet for ventricular blood-pool segmentation by introducing a bottleneck block and an upsampling path. Our experiments show that the proposed architecture runs on the Automated Cardiac Diagnosis Challenge (ACDC) dataset using half (50%) the memory requirement of DenseNet and one-twelfth (∼ 8%) of the memory requirements of U-Net, while still maintaining excellent accuracy of cardiac segmentation. |
|
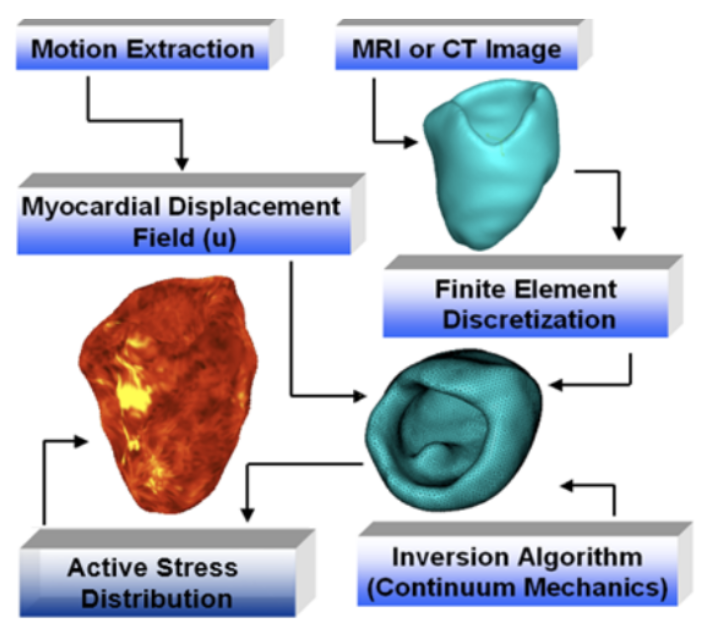
Toward Quantification and Visualization of Active Stress Waves for Myocardial Biomechanical Function Assessment. Niels F Otani, Dylan Dang, Christopher Beam, Fariba Mohammadi, Brian Wentz, S. M. Kamrul Hasan, Suzanne M Shontz, Karl Q Schwarz, Sabu Thomas, and Cristian A. Linte. Computing in Cardiology (CinC), 2019. [paper][code][dataset][bibtex] In the forward model, tissue deformation was generated using a test wave with active stresses that mimic the myocardial contractile forces. The generated deformation field was used as input to an inverse model designed to reconstruct the original active stress distribution. We numerically simulated malfunctioning tissue regions (experiencing limited contractility and hence active stress) within the healthy tissue. We also assessed model sensitivity by adding noise to the deformation field generated using the forward model. The difference image between the original and reconstructed active stress distribution suggests that the model accurately estimates active stress from tissue deformation data with a high signal-to-noise ratio. |

|
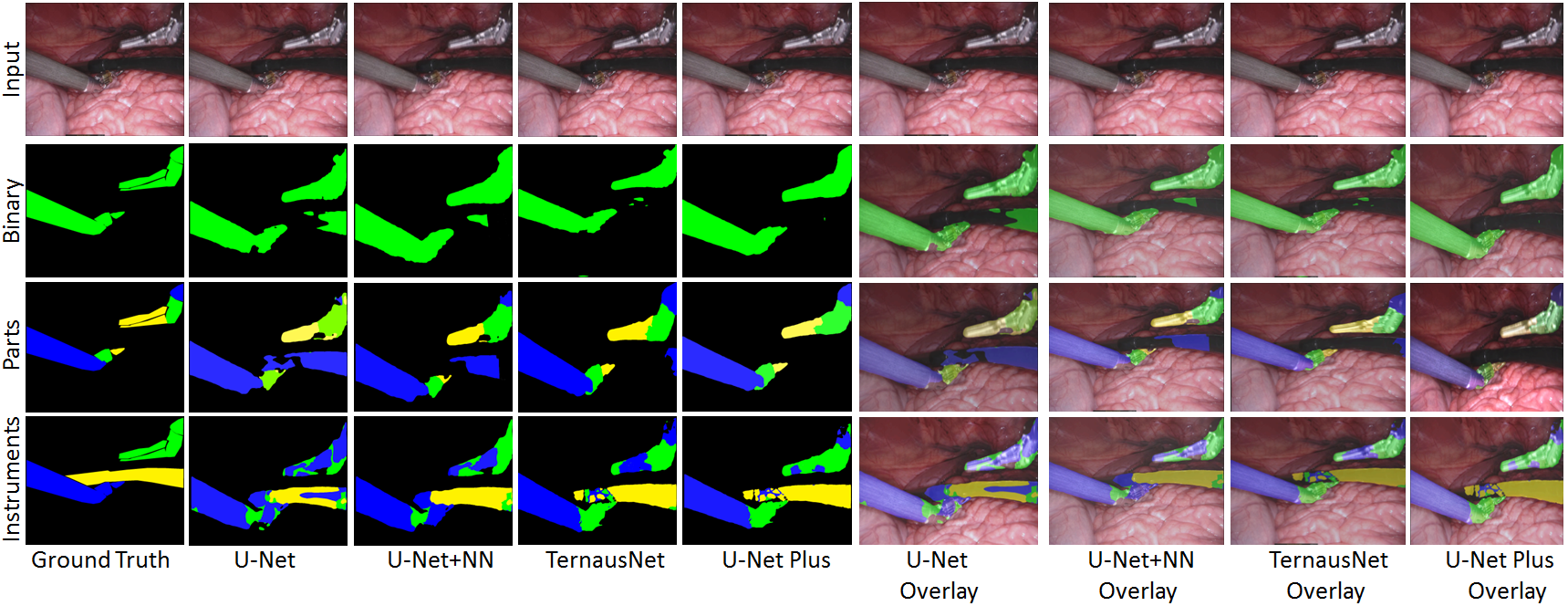
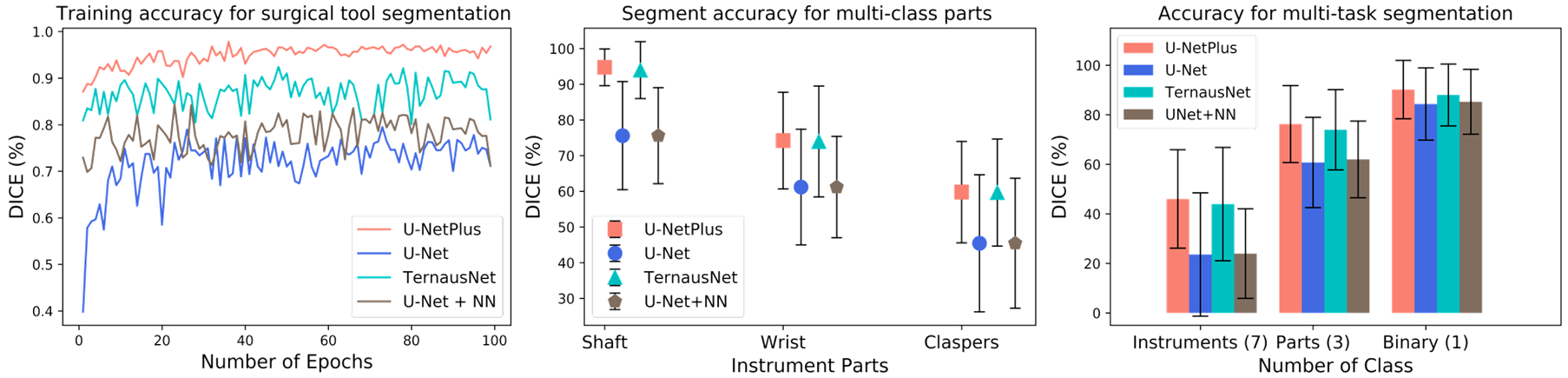
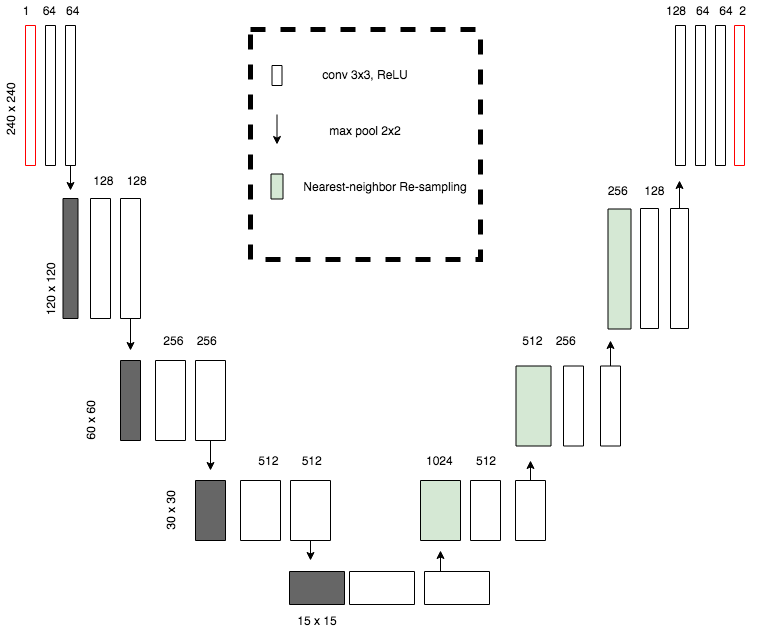
U-NetPlus: A Modified Encoder-Decoder U-Net Architecture for Semantic and Instance Segmentation of Surgical Instruments from Laparoscopic Images. S. M. Kamrul Hasan, and Cristian A. Linte. International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology (EMBC), 2020, oral [paper][code][dataset][bibtex] In this work, we modify the U-Net architecture by introducing a pre-trained encoder and re-design the decoder part, by replacing the transposed convolution operation with an upsampling operation based on nearest-neighbor (NN) interpolation. To further improve performance, we also employ a very fast and flexible data augmentation technique. We trained the framework on 8 x 225 frame sequences of robotic surgical videos available through the MICCAI 2017 EndoVis Challenge dataset and tested it on 8 x 75 frame and 2 x 300 frame videos. Using our U-NetPlus architecture, we report a 90.20\% DICE for binary segmentation, 76.26% DICE for instrument part segmentation, and 46.07% for instrument type (i.e., all instruments) segmentation, outperforming the results of previous techniques implemented and tested on these data. |

|
A Modified U-Net Convolutional Network Featuring a Nearest-neighbor Re-sampling-based Elastic-Transformation for Brain Tissue Characterization and Segmentation. S. M. Kamrul Hasan, and Cristian A. Linte. Western New York Image and Signal Processing Workshop (WNYISPW), 2018, oral [paper][code][dataset][bibtex] Though this model works better on BRATS 2015 dataset by using pixel-wise segmentation map of the input image like an auto-encoder which assures best segmentation accuracy, but it is not correct for all the cases. So, I have planned to improve this U-net model by replacing the de-convolution part with the upsampled by Nearest-neighbor algorithm and also by using elastic transformation for increasing the training dataset to make the model more robust on Low graded tumor. I had trained my NNRET U-net model on BRATS 2017 dataset and got a better performance than the state of the art classic U-net model. |
| 2022 | Podcast | Bangladeshi Researchers in Data Science and Machine Learning |
| 2021 | Presentation | Philips Research North America |
| 2021 | Workshop | RIT Co-op Placement (Guest Speaker) |
| 2020 | Presentation | IBM Almaden Research Center |